
What Is a Soil Survey, How Is It Done? Guide and Prices
by Rabia Tosun - October 28, 2025The strength of a building depends not only on materials and architecture but also directly on the condition of the ground it stands on. A soil survey is a scientific process that examines the geological and technical characteristics of the land where construction will take place. This process helps reduce earthquake risk, ensures proper foundation design, and increases the longevity of the structure.
The survey includes drilling, laboratory tests, soil classification, and bearing capacity calculations. It is not only an engineering task but also a critical element of urban planning and risk management.
An incomplete or incorrect survey can lead to cracks, settlement, and serious costs. Therefore, it is vital to work with a qualified firm, correctly interpret the report, and evaluate prices carefully.
This guide explains step by step what a soil survey is, how it is carried out, and what to look for in the report helping you make more informed decisions for your project.
What Is a Soil Survey?
A soil survey is a scientific study that analyzes the physical and technical properties of the land where a structure will be built. The goal is to design a safe and suitable foundation for the ground. This process evaluates not only the soil type but also factors such as groundwater level, bearing capacity, and soil behavior.
In Turkey, soil surveys are mandatory for obtaining a building permit under Earthquake and Disaster Regulations. Reports can only be prepared by authorized engineering firms and must be approved by municipalities.
In short, a soil survey is the most critical initial step of any construction project. If conducted improperly, even the most solid building can face ground-related problems. In residential projects in Antalya, soil surveys are of vital importance due to the region’s alluvial soil structure.
Why Should a Soil Survey Be Conducted?
There are three main reasons for conducting a soil survey:
Safety: Ground data is essential for designing earthquake-resistant foundations.
Economy: A proper survey prevents unnecessary foundation costs.
Legal Requirement: Building permits cannot be issued without an approved report.
In conclusion, a soil survey is not merely a legal formality but an indispensable process that guarantees the durability and longevity of a building.
How Is a Soil Survey Conducted?
A soil survey is a systematic field and laboratory study used to determine whether the land is suitable for construction. The process consists of preliminary research, drilling, sampling, laboratory tests, geophysical measurements, and reporting. Each stage helps engineers better understand the physical and dynamic behavior of the soil.
According to current regulations, seismic analyses (such as Vs30, MASW, and microtremor) are now mandatory. This allows evaluation not only of the surface but also of the deeper layers of the ground.
In short, a soil survey is far more than just a few drillings; it is a detailed and scientific collaboration between engineering and nature. In regions like Aksu and Altıntaş, where groundwater levels and bearing capacities vary, drilling depths typically exceed 20 meters.
Stages of the Soil Survey Process
A soil survey usually consists of six main stages:
- Preliminary Study and Site Inspection: Examination of geological maps, topography, and previous survey data.
- Drilling Operations: Boreholes are typically drilled to depths of 10–30 meters. Soil type and moisture content are recorded at each meter.
- Sampling (SPT, UD): The Standard Penetration Test (SPT) determines soil density, and undisturbed samples are collected.
- Geophysical Measurements: Seismic refraction, MASW, or microtremor methods are used to measure wave velocities.
- Laboratory Analyses: Grain size distribution, Atterberg limits, water content, and unit weight are tested on samples.
- Engineering Evaluation and Reporting: All data are combined to determine bearing capacity, soil class, liquefaction potential, and foundation recommendations.
These stages allow engineers to model the soil as a reliable structural material.
Equipment and Techniques Used
Both field and laboratory equipment are utilized during soil surveys. In the field, drilling rigs, SPT tools, geophones, and seismographs collect soil data. In the laboratory, sieve sets, Atterberg limit devices, and triaxial test systems analyze soil classification and behavior.
Modern digital systems enable direct data transfer into reporting software, speeding up the process and minimizing errors.

What Does a Soil Survey Report Include?
A soil survey report is the “identity document” of a land from an engineering perspective. It is a scientific document that interprets all drillings, measurements, and laboratory results. Civil engineers, architects, municipal authorities, and contractors use this report to understand the ground’s properties and determine the building requirements.
As of 2025, the Ministry of Environment, Urbanization, and Climate Change has standardized all soil survey reports through the Soil and Foundation Survey Report Format Standard. This ensures consistent technical content and comparable results across projects.
A soil survey report is not merely a data summary but a rationale for engineering decisions. Its scientific accuracy and linguistic clarity are equally important.
Report Format and Data Provided
A typical soil survey report consists of five main sections:
- General Information: Project name, location, coordinates, client information, and scope.
- Geological and Geotechnical Review: Field observations, topography, geological units, groundwater level.
- Field and Laboratory Test Results: Borehole logs, SPT values, grain size distribution, and Atterberg limits.
- Engineering Evaluation: Soil class, bearing capacity, settlement analysis, liquefaction analysis.
- Results and Recommendations: Foundation type selection, improvement suggestions, risk assessment.
Reports also include cross-section drawings, maps, graphs, and photos. As of 2025, digital reports must include QR codes or digital signatures to prevent forgery a crucial safety measure.
The Role of Soil Surveys in Building Permits
To obtain a construction permit, a soil survey report must be approved by the municipality. It serves as the main data source for designing load-bearing systems like columns and foundations. Incomplete or inaccurate reports can halt the permitting process.
Municipalities now manage approvals through the digital ZEBS platform. Authorized firms upload their reports, and the system automatically detects errors. Approved reports become mandatory documents for building permit applications.
Who Conducts Soil Surveys?
Soil surveys can only be conducted by engineering firms authorized by the Ministry of Environment, Urbanization, and Climate Change. These firms must employ engineers specialized in geology, geophysics, or civil engineering, all registered with the Turkish Chamber of Engineers (TMMOB).
A typical team includes geological engineers analyzing soil composition, geophysical engineers assessing seismic properties, and civil engineers designing the foundation system based on the data. The entire process is carried out collaboratively across disciplines.
Municipalities accept only reports from Ministry-approved firms, ensuring both engineering quality and data reliability.
Authorized Institutions and Firms
Authorized entities for soil surveys include private engineering firms, public institutions (such as İller Bankası, TOKİ, and DSİ), and university laboratories. Private firms must obtain a Soil and Foundation Survey Application Competency Certificate, based on their technical equipment, engineering staff, and laboratory infrastructure.
As of 2025, the Ministry has published a public online list of these firms on the Soil Survey Firms Information System (ZEFiS). Citizens can search by province and verify firm credentials or reports, ensuring transparency and quality control.
Required Documents for Authorized Firms
To legally conduct soil surveys, a firm must hold the following documents:
- Trade Registry and Tax Certificate
- Ministry-Approved Soil and Foundation Survey Authorization Certificate
- Chamber Registrations for Geological, Geophysical, and Civil Engineers
- Laboratory Competency Certificate (TÜRKAK or equivalent)
- List of insured personnel and equipment inventory
Municipalities verify these documents through ZEFiS during approval, effectively preventing unlicensed or fake reports.
Soil Survey Prices
Soil survey prices are not fixed; they vary according to project type, land structure, and drilling depth. The primary cost factor is soil complexity. For instance, drilling in rocky terrain is more difficult and thus more expensive. Similarly, multi-story buildings require more extensive studies than single-story ones.
The Soil and Foundation Survey Service Fee Regulation, updated at the end of 2024, defines the 2025 price ranges. Pricing is based on factors such as drilling number and depth, laboratory test count, and geophysical measurement type. Urban projects are generally cheaper due to lower logistics costs, while rural or sloped terrains increase expenses.
In short, soil survey prices depend not on square meters but on engineering requirements.
Factors Affecting Soil Survey Costs
Several factors influence the total cost:
- Drilling Depth and Number: Each additional meter increases both labor and lab costs.
- Soil Type: Hard rock or water-saturated soils take longer to test.
- Laboratory Tests: The number of analyses (grain size, Atterberg limits, triaxial test, etc.) determines total cost.
- Geophysical Method: Prices differ among MASW, microtremor, and seismic refraction methods.
- Location and Accessibility: Remote or sloped sites require higher setup costs.
Every soil survey is thus a uniquely priced engineering service.
Average Prices by Building Type
Because building type determines survey scope, prices also vary accordingly. Average market values are:
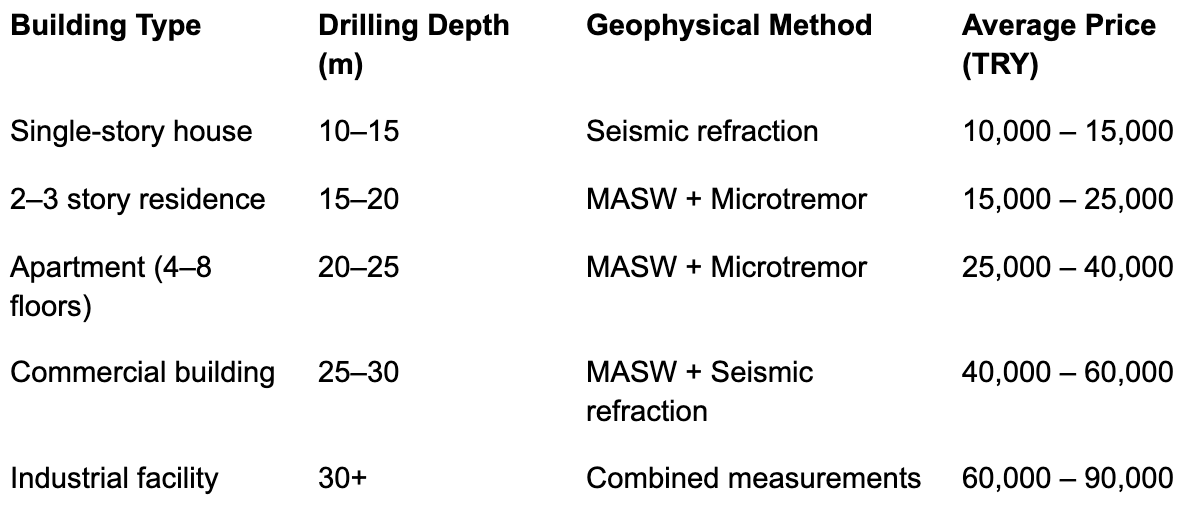
These figures reflect 2025 national averages published by engineering chambers. When requesting quotes, firms’ authorization and laboratory certificates should always be verified.
How to Verify a Soil Survey Report
Once completed, a soil survey report can be verified through e-Government (e-Devlet), the Ministry of Environment, Urbanization, and Climate Change, or municipal systems. This allows both property owners and local authorities to confirm the report’s validity.
The verification system is a safety measure to prevent false or incomplete reports. All approved reports are digitally stored in the Ministry’s ZEBS (Soil Survey Information System) database, accessible online for public verification.
Verification via e-devlet and Related Platforms
To verify a soil survey report via e-devlet:
- Log into the e-devlet homepage.
- Type “Zemin Etüt Bilgi Sistemi (ZEBS)” in the search bar.
- Select “Soil Survey Report Inquiry.”
- Enter the report number or parcel information.
The system displays approval status, preparation date, authorized firm details, and coordinate data. Users can also download the PDF copy of the report.
The Ministry developed this service to enhance public oversight and administrative transparency, allowing even apartment owners to check their building’s survey authenticity.
Accessing Soil Survey Archives
Soil survey archives are stored both digitally and physically. Digital archives can be accessed via ZEBS or municipal zoning archive systems. Especially in major cities, all reports prepared after 2019 have been uploaded as scanned PDFs.
Physical archives are kept in municipal zoning departments and can be accessed using parcel numbers or project names. Although old reports can serve as references for new projects, each new construction still requires a fresh on-site soil survey.
This system strengthens both urban safety and engineering data integrity.
The First Step in Structural Safety: Accurate Soil Surveys
The safety of a structure begins with sound engineering fundamentals. A soil survey is not merely a report it is a scientific guide that determines the lifespan of a building. A proper survey reduces earthquake risks, optimizes foundation design, and ensures investment sustainability.
As of 2025, regulations have made soil surveys mandatory for all projects effectively a safety guarantee. A professionally prepared soil survey not only accelerates the permit process but also minimizes structural risks.
Underestimating a soil survey means leaving a building’s future to chance; relying on science is the only way to protect both life and property.
Professional Soil Survey Services
Do not leave your building’s safety to chance. At Yükselen Mimari, we provide professional soil survey solutions in full compliance with the latest regulations and laboratory standards. Through customized analysis, on-site measurements, and digital reporting systems, we manage the entire process efficiently, transparently, and reliably.
Whether for individual residences or large-scale commercial buildings, an accurate soil survey is the foundation of your project’s success.
Contact us today, and our engineering team will provide the most suitable survey plan and quotation for your project.

